DATE
December 27, 2022
CATEGORY
Blog
SHARE

Industrial Revolution 4.0: An Introduction
The Industrial Revolution is the transition to a new manufacturing process, shifting the way business operates and use machinery. Technology and machinery have greatly shaped the way modern companies operate, manufacture, and distribute. Modern businesses work due to the fourth industrial revolution, also referred to as “4IR-Industry revolution 4.0”.
The 21st century marks the beginning of another industrial revolution. The fourth industrial revolution has blurred the lines between the physical, digital, and biological worlds by integrating new technologies. The Internet of things (IoT), cloud computing and analytics, artificial intelligence, machine learning, gene editing, and advanced robotics are all new and disruptive technology under the fourth industrial revolution. As a result of these technologies, real-time decision-making, productivity, flexibility, and agility have increased many folds.
A few typical examples of Industry Revolution 4.0 are:
- Analyzing large amounts of data sets collected through sensors ensures real-time visibility of manufacturing assets and reduces equipment downtime in the manufacturing sector.
- Using advanced robotics in healthcare makes patients experience quick recovery and seamless treatment.
- Using high-end IoT devices in smart factories resulted in higher productivity and improved product quality.
- Using AI-powered business models for visual insights into inspection and quality review reduces manufacturing errors and saves money and time.
- Augmented reality entering the entertainment sphere.
Figure 1: Pillars of the Fourth Industrial Revolution
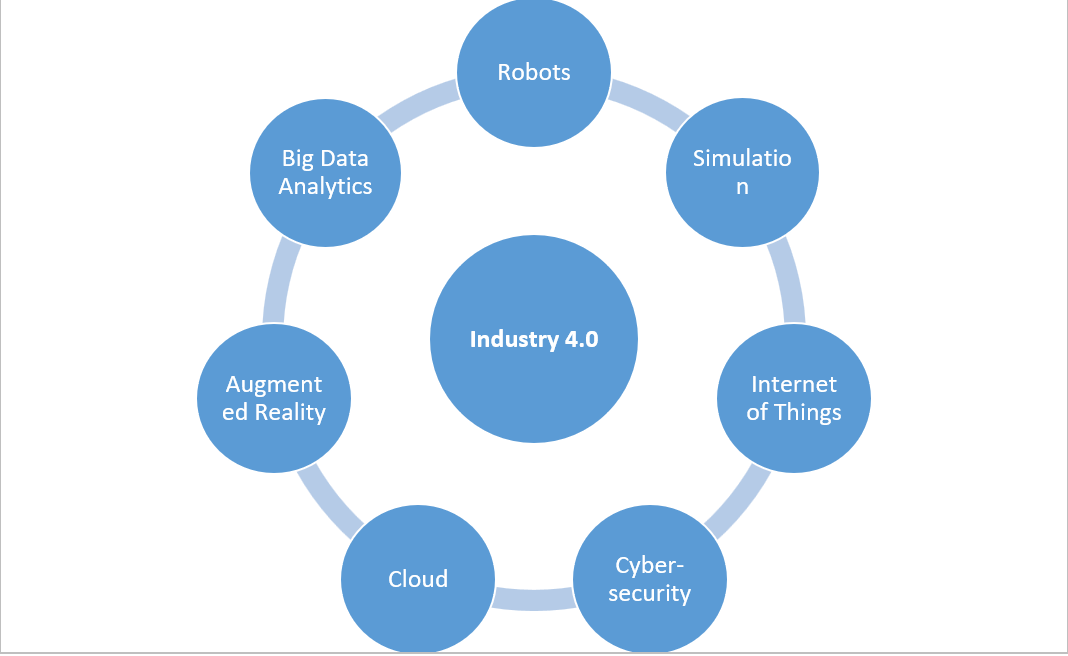
In the past, humankind has experienced three industrial revolutions, with each revolution the zeal to increase machine-based algorithms to generate error-free products with less time consumption increases. Thus, giving rise to interconnected technology.
Characteristics of 4IR:
- Interconnectivity
- Machine-to-machine Interface
- Big Analytics
- Wearable
- Simulation
- Genetic Engineering
- Nanotechnology
- Artificial Intelligence
Table 1: Different Industrial Revolutions
| Revolution | Time-period | Key Points |
| First | · 1760–1820 | · The First Industrial Revolution was when hand production methods were discarded, and instead, machines were used which used steam and water power. |
| Second | · 1871–1914 | · The Second Industrial Revolution, or the Technological Revolution, resulted in the installation of extensive railroad and telegraph networks globally, allowing for faster transfer of people, ideas, and electricity. |
| Third | · Late 20th Century | · Digital Revolution was when supercomputers were introduced. |
| Fourth | · 21st Century | · The Fourth Industrial Revolution is currently in its preliminary stage with automation and data exchange and processes, including cyber-physical systems, IoT, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence. |
MENA region consists of countries in the Gulf and part of North Africa, namely Bahrain, Egypt, Israel, Jordan, Morocco, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates, among others.
In the recent past, an upsurge of technology in the MENA region has led to the momentum around policies that maximize the benefits of 4IR.
Some of the policies in place for integrating newer technology in the MENA region:
Table 2: Few of the Industry 4.0 Initiatives Launched in the Middle East and North Africa
| Country | Industry 4.0 Initiatives | Year |
| Israel | · Israel 2028 | · 2018 |
| · Israel Innovation Report 2017 | · 2015 | |
| · Startup Nation | · 2012 | |
| UAE | · Smart Dubai 2021 | · 2017 |
| · UAE AI Strategy 2031 | · 2018 | |
| · UAE’S National Agenda 2021 | · 2016 | |
| Saudi Arabia | · Saudi Vision 2030 | · 2016 |
| · KSA’s National Transformation Plan 2020 | · 2016 | |
| Qatar | · Qatar National Vision 2030 | · 2016 |
| · Qatar’s National Development
Strategy 2017–2022 |
· 2017 | |
| Kuwait | · New Kuwait Vision 2035 | · 2016 |
| Morocco | · Digital development agency
(L’Agence de Développement Digital) (ADD) |
· 2017 |
Industrial Revolution 4.0: Impacts on Medical Device Technology
Like all other industries, the fourth industrial revolution has also greatly influenced the medical device sector. Technology-rich solutions have greatly impacted areas such as diagnosis, patient data storage, and the physician–patient relationship.
Components of Industrial Revolution 4.0 That are Being Harnessed in Medical Device Technology in MENA are:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Abbreviated as AI/ML, is the technology that can transform healthcare by deriving new and important insights from the vast amount of data generated daily. AI uses different techniques, including models based on statistical data analysis, whereas ML is an artificial intelligence technique used to design and train different software algorithms to learn from the vast amount of data.
Medical device manufacturers in the MENA region are using AI/ML technologies to improvise their products to assist healthcare providers better and improve the patient care experience. A few examples include:
Diginova is registered with Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) and is a leading financial hub in the Middle East, Africa, and South Asia. It has patterned with Biovista Personalized Medicine, a US-based pioneer of AI and systemic drug repositioning for its “AI Health Shield” technology in the MENA region.
AI Health Shield is a platform that helps doctors provide quality care and the best possible treatment for patients. The platform uses massive health research data and analytics to match any medical condition and healthcare scenario. It is the best alternative when the patient is not responding to the standard treatment or requires speedy recovery. Additionally, AI Health Shield leaves no stone unturned in treatment by offering over 270,000 clinical outcomes against all known therapies and delivering results based on the research data and outcomes to examine every approved drug for the condition.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing is a subscription-based infrastructure that delivers services such as storage, databases, software, and networking. Cloud-connected systems are rapidly emerging in medical device service providers. Using the technology, the medical device collects data for storage, computation, accessibility, and sharing, all performed wirelessly. Additional features of cloud computing are, detecting data breaches and allowing for backup and recovery.
Furthermore, with wearable technology surging in popularity in MENA, cloud computing is simultaneously growing.
Such as, a partnership between Microsoft and Roche is leveraging AI and cloud solutions, redefining healthcare possibilities in the Middle East. In December 2021, Roche agreed to use Microsoft AI and cloud technology to improve outcomes for patients across the Middle East and help healthcare providers with the early adoption of new diagnostic tools.
Beginning in Egypt, the collaboration will be rolled across countries, including the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Lebanon, Jordan, Kuwait, Oman, Bahrain, Iraq, and Syria.
- Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G: The huge surge in demand for IoT could be realized as it is one of the key components of the fourth industrial revolution. IoT is internet/web-enabled objects that transfer data and communicate with each other. Wearable smart devices are a few of the IoT devices. IoT receives data through sensors and processes and stores that data through web-enabled means. IoT also uses artificial intelligence and machine learning so that data-collecting processes are done swiftly and remain dynamic. IoT will have an even stronger grip on consumers with the rollout of 5G (fifth-generation) technology which is the planned successor to the 4G networks and provides swift connectivity to smart devices. Commercial 5G networks were launched in six MENA countries, Bahrain, Kuwait, Qatar, Oman, Saudi Arabia, and UAE, between 2018 and 2020.
In the medical device sector, many devices and wearables are smart devices, changing the landscape of healthcare as they provide freedom of remote patient monitoring. This type of patient care experience through connected devices and IoT sensors provides a continuous stream of real-time health data such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose monitoring to the patient and the physician.
A person wearing a smartwatch to track their heart rate, a neurostimulator in the brain, or continuous glucose monitoring of a diabetic patient are all examples of IoT.
Figure 2: Examples of IoT Medical Devices
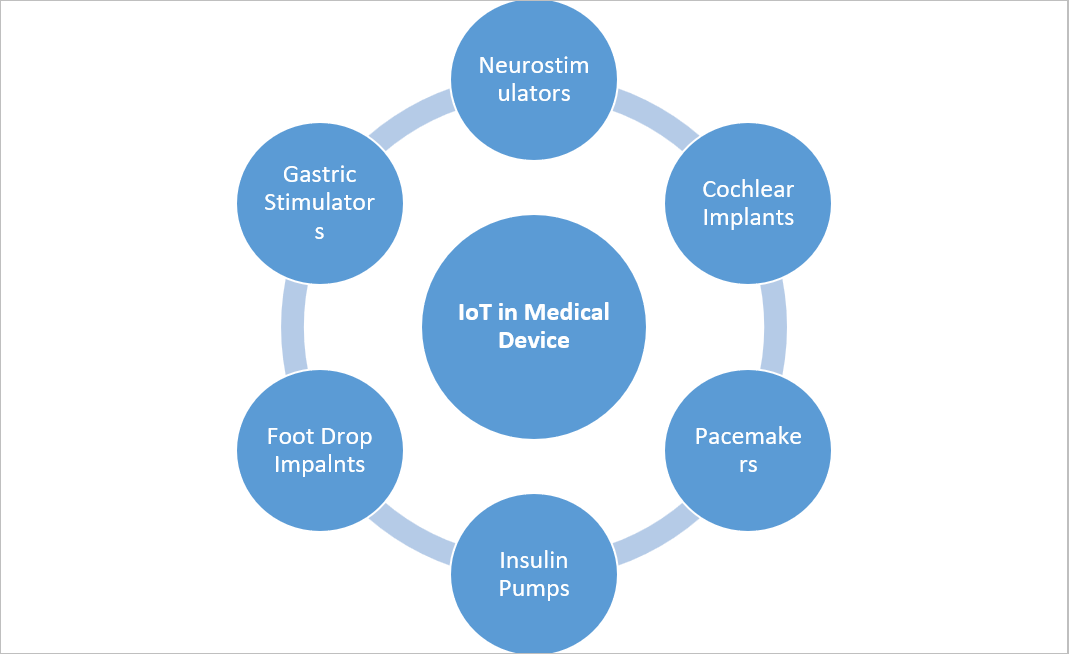
Moving ahead, this connected technology has changed its shape from merely wearable to smart hospitals. Multiple hospitals have started to roll out smart beds. These beds can sense the presence of a patient and can automatically adjust themselves to the correct position, angle, and pressure to provide proper support to the patient without the need for a nurse to intervene.
UAE currently leads the smart hospitals market in the Middle East, with Fakeeh University Hospital, which will be a smart hospital. Some of the facilities in the hospital are tablets in each patient’s room to communicate with medical staff and control their surroundings, which also ensures social distancing. A dedicated app for the hospital allows doctors to monitor the progress of their patients around the clock through a control center. Global technology firms Phillips, Siemens, and Cisco, have also come on board with partnerships to equip the smart hospital with medical technology solutions.
Other initiatives on the cards include Middle East’s first virtual hospital, powered by video conferencing and monitoring tools for remote examination, while patients can stay home. Smart ambulances, which can turn signals on the road green and relay real-time data to hospitals, are also set to hit the MENA market.
- Robotics: Medical robotics is an emerging field in healthcare, which consists of markets for exoskeletons, care robots, and hospital robots currently in the infancy stage of market development. The market will eventually see rapid increases in surgical procedures, which will give rise to more installed base surgical systems within hospital institutions. Hospitals like Sharjah’s Al Qassimi in Dubai use robots to remove tumors. MENA Robotics is an enterprise launched in 2015 that aims to build new scientific and business communities in the emerging field of robotics in MENA. All this ecosystem is paying the way for more and more advancements in the robotics arena in the MENA region. Reliable Robotics LLC is Middle East’s leading robotics company, founded in 2018 and headquartered in Dubai, UAE.
Populations that will be benefitted from Industry Revolution 4.0 in MENA:
- As per the Globocan statistics (2020), the number of cancer cases in Saudi Arabia accounted for about 27,885 people, and the number of deaths due to cancer was 13,069. As per the above source, the number of cancer cases in the United Arab Emirates was nearly 4,807 in 2020, with breast cancer having the maximum number of cases. Also, in the same year, 1,215 cases of cancer were observed in Bahrain. Thus, this high number of cancer patients could benefit from the fourth industrial revolution through robotics.
- According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), the adult diabetes prevalence in 2020 was 18.3% in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Arabia is the seventh-highest country for new cases of Type 1 diabetes every year; it is estimated that the number will increase from 4,274 to 7,537.3 in 10,000 people by 2045. However, diabetes could be managed using connected technology, such as smart wearables, allowing continuous glucose monitoring.
- As per the survey conducted by Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi (2021), 55% of respondents from 1,000 UAE residents were directly affected by heart disease. Any irregular heart rhythm could be easily tracked through sensors which will send real-time data to cardiologists and even alert the concerned authorities in case of a heart attack.
- According to United Nations Population Fund data, in Saudi Arabia, the population aged 60 and above is expected to increase fivefold during 2020–2050, from 2 million to 10.5 million. A high number of geriatric population can have care robots alongside them, which will dramatically cut the cost of nursing elderly patients because extended families are dispersing and a growth in nuclear families is seen lately; moreover, social welfare budgets are under strain.
- Moreover, the COVID-19 outbreak led to a sense of urgency and panic among people worldwide, including in the MENA region. Therefore, in such scenarios, virtual hospitals will assist patients in treating and managing diseases in homecare settings, thereby avoiding hospital visits and thus reducing the transmission of viral infection.
Industrial Revolution 4.0 in MENA: The Road Ahead
The Fourth Industrial Revolution represents a fundamental change in the operation of the healthcare industry. It is a new human development chapter and is only in the beginning phase. The disruptive technologies will reduce misdiagnosis and open new horizons as IBM Watson can classify large amounts of data, including clinical knowledge, case histories, and molecular and genomic data that can help oncologists diagnose and treat cancer. Unlike traditional big data systems, Watson understands data through AI, promoting better data processing and analysis and generating new knowledge. Surgery 4.0 currently incorporates various technologies, such as robotics, big data, and IoT technologies; it is as safe and effective as traditional surgery in certain diseases and even safer in other diseases. This surgery allows the patient to recover faster because it is less invasive.
Although new technologies can provide better outcomes, they also have certain challenges and limitations. One of the major areas of concern is the aggregation of many medical datasets that pave the way for security concerns. Personal clinical data could be breached or hacked; thus, newer and stringent regulatory norms concerning medical data protection should be placed.
The other challenge with the fourth industrial revolution is the regulatory process. New regulatory and approval processes must be incorporated in the healthcare field with telehealth, wearable, and robotics in medical devices. The guidelines should be laid so that the consumer and the manufacturer could reap the most benefit from the industrial revolution.
Lastly, government bodies play a major role in adopting newer technologies in the country. The role of government should be proactive in laying down new foundations and policies to maximize the full potential of the 4IR, as this is just the beginning.
Source: http://www.delveinsight.com/